India is one of the largest countries in South Asia and shares its borders with 9 countries, out of which 7 countries share their land boundary and two countries share their maritime boundary. Understanding the neighbouring countries of India is important for geography, UPSC, SSC, and other competitive exams, as well as for general awareness. India’s geographical location makes it strategically significant in Asia, connecting South Asia with Central Asia, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
This article provides a detailed overview of the neighbouring countries of India, including their borders, capital cities, geographical importance, and India’s relations with them.
Neighbouring Countries of India
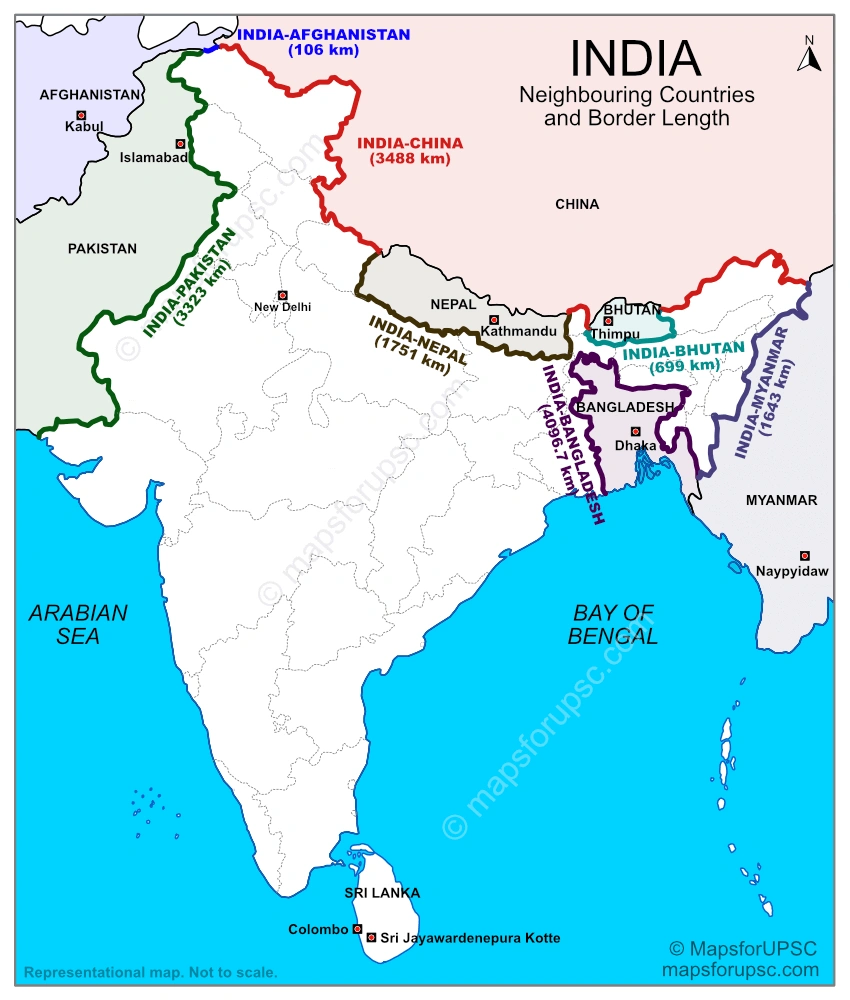
India shares land borders with seven countries: Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Myanmar and maritime boundaries with Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Bangladesh shares the longest land border with India at 4,096.7 km, followed by China (3,488 km), Pakistan (3,323 km), Nepal (1,751 km), Myanmar (1,643 km), and Bhutan (699 km), while Afghanistan shares the shortest border of 106 km. Sri Lanka lies to the south of India, separated by the Palk Strait, whereas the Maldives is located southwest of India in the Indian Ocean. These neighbouring countries play a crucial role in India’s geographical, cultural, and strategic significance in South Asia.
Neighbouring Countries of India With Capital List
India shares its international boundaries with 9 countries through land and maritime borders. These neighbouring countries play an important role in India’s geopolitics, trade relations, security concerns, and cultural connections. Below is a detailed list of Neighbouring Countries of India With Capital.
| Country | Capital | Border Length with India | Indian States Sharing Border |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Kabul | 106 km | Ladakh (Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir region) |
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | 4096.7 km | West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram |
| Bhutan | Thimphu | 699 km | Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh |
| China | Beijing | 3488 km | Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh |
| Myanmar | Naypyidaw (Administrative), Yangon (Former Capital) | 1643 km | Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram |
| Nepal | Kathmandu | 1751 km | Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim |
| Pakistan | Islamabad | 3323 km | Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat |
| Sri Lanka | Colombo (Commercial Capital), Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte (Legislative Capital) | Maritime Border | Separated from India by the Gulf of Mannar |
| Maldives | Malé | Maritime Border | Located southwest of Lakshadweep Islands in the Indian Ocean |
9 Neighbouring Countries of India: Key Highlights
India shares borders with nine countries through land and sea, making these neighbours strategically, culturally, and economically significant. These neighbouring nations influence India’s foreign policy, regional cooperation, trade relations, and security framework.
1. Pakistan
Pakistan shares a 3323 km long land border with India along the western frontier. The relationship is strategically sensitive due to historical conflicts, security concerns, and diplomatic challenges. India shares its border with Pakistan across Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat. The India-Pakistan border includes the Line of Control (LoC) and the International Border. Relations between the two countries have been marked by historical conflicts, especially over the Kashmir issue, along with concerns related to cross-border terrorism and security tensions.
2. Afghanistan
Afghanistan shares a 106 km boundary with India through the Ladakh region (via Pakistan-occupied Kashmir). It is strategically important for India’s connectivity to Central Asia and regional stability. Although India does not have direct physical access to Afghanistan due to Pakistan, Afghanistan remains a crucial partner in India’s foreign policy. India has invested heavily in Afghanistan’s infrastructure, education, healthcare, and development projects. Afghanistan acts as a strategic bridge connecting India to Central Asian nations rich in natural resources.
Also Read: Ramsar Sites in India
3. China
China shares a 3488 km long border with India along the Himalayan region. India-China relations involve both economic cooperation and strategic competition. India shares its border with China through Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh. The border is known as the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which has been a point of tension between the two countries. China is one of India’s largest trading partners, contributing significantly to bilateral trade and economic engagement. However, border disputes and geopolitical competition influence diplomatic relations.
4. Nepal
Nepal shares a 1751 km long open border with India. The relationship is characterised by strong cultural, religious, and economic ties. India and Nepal share borders across Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim. One of the unique features of India-Nepal relations is the open border system, allowing free movement of people and goods. The two countries share deep cultural connections rooted in Hinduism and Buddhism. Nepal is strategically located between India and China, making it significant for regional security and diplomacy.
5. Bhutan
Bhutan shares a 699 km border with India and is considered one of India’s closest and most trusted allies. The relationship is based on strong diplomatic, economic, and security cooperation. India shares its border with Bhutan through Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh. Bhutan plays a vital role in India’s Himalayan security strategy. India supports Bhutan’s hydropower sector, which contributes significantly to Bhutan’s economy. The two countries maintain strong diplomatic trust and cooperation in defence and foreign policy matters.
6. Bangladesh
Bangladesh shares the longest land border with India, measuring 4096.7 km. It is one of India’s most important trade and regional connectivity partners. India shares borders with Bangladesh through West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram. India and Bangladesh share deep historical, linguistic, and cultural ties. Bangladesh is a major trading partner and plays a key role in strengthening connectivity between mainland India and the northeastern states. The two countries cooperate in water sharing agreements, border security, counter-terrorism, and infrastructure projects.
7. Myanmar
Myanmar shares a 1643 km border with India and acts as India’s gateway to Southeast Asia. It is central to India’s Act East Policy. India shares its border with Myanmar through Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram. Myanmar is strategically important for strengthening India’s trade and connectivity with ASEAN countries. The two countries collaborate on infrastructure projects such as highway construction and cross-border trade routes. Myanmar also plays a crucial role in managing border security and insurgency-related challenges in India’s northeastern region.
8. Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is separated from India by a maritime boundary across the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait. It is strategically important for India’s Indian Ocean security and trade routes. Sri Lanka does not share a land border with India but remains one of India’s closest maritime neighbours. The two countries share strong cultural and historical connections, especially through Buddhism and ancient trade relations. Sri Lanka holds strategic importance due to its location near major global shipping routes.
9. Maldives
Maldives shares a maritime boundary with India and is located southwest of Lakshadweep Islands in the Indian Ocean. It plays a key role in India’s maritime security and regional diplomacy. Maldives is an island nation strategically located along major international sea routes. India maintains strong diplomatic, defence, and economic relations with Maldives under its “Neighbourhood First” policy. India has assisted Maldives in disaster management, defence cooperation, and infrastructure development projects.
Longest Border of India with which Country
India shares its longest international land border with Bangladesh, stretching about 4,096.7 km along the eastern side of the country. This border passes through several Indian states and is important for trade, cultural exchange, and connectivity. The India-Bangladesh border was further stabilized after the Land Boundary Agreement 2015, which resolved long-standing territorial disputes.
Smallest Border of India with which Country
India shares its shortest land border with Afghanistan, measuring approximately 106 km. This border lies in the north-western region of India in the Union Territory of Ladakh (area of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir). Despite its short length, the border holds strategic importance for India’s connectivity with Central Asia.
Bordering States of India
Several Indian states share international boundaries with neighbouring countries, highlighting India’s geographical diversity. States like West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram share borders with Bangladesh, while Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Jammu & Kashmir share borders with Pakistan. Similarly, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Ladakh share borders with China, Nepal, Bhutan, and Myanmar.