The Group of Twenty (G20) is a premier international forum for economic cooperation and policy coordination among major advanced and emerging economies. Established in 1999 in the wake of the Asian financial crisis, the G20 brings together the world’s largest economies to discuss global financial stability, sustainable development, trade, and investment issues.
G20 Countries
The G20 Countries consist of 19 individual nations and the European Union, making it a unique group that blends both developed and developing economies. Its rotating presidency allows each member to host the annual G20 Summit, where leaders discuss pressing global issues like inflation, climate change, digital economy, and global health.
G20 Countries Overview
The core framework of the G20 Countries. They were created to promote international financial stability and prevent future global economic crises through cooperative dialogue among the world’s largest economies.
| G20 Countries Overview | |
| Aspect | Details |
| Full Name | Group of Twenty (G20) |
| Founded | 1999 (at Finance Ministers’ level), First Leaders’ Summit in 2008 |
| Headquarters | None (rotational presidency) |
| Members | 19 countries + European Union |
| Representation | ~85% of global GDP, 75% of global trade, ~66% of world population |
| Permanent Invitee | Spain |
| Annual Presidency | Rotates among members |
| Key Event | G20 Leaders’ Summit |
List of G20 Countries (As of 2025)
The G20 comprises a diverse mix of nations, representing every inhabited continent. The combination of advanced and emerging economies ensures a balanced representation of global economic interests.
| List of G20 Countries (As of 2025) | |
| Continent | G20 Member Countries |
| Asia | China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Saudi Arabia, South Korea |
| Europe | France, Germany, Italy, United Kingdom, Turkey, Russia, European Union |
| North America | United States, Canada, Mexico |
| South America | Argentina, Brazil |
| Africa | South Africa |
| Oceania | Australia |
Objectives of G20 Countries
The G20 Countries work toward economic stability, financial inclusion, environmental protection, and equitable global development. Though informal, their outcomes shape international policies and institutional reforms.
| Objectives of G20 Countries | |
| Objective | Explanation |
| Promote Global Economic Stability | Prevent financial crises and enhance macroeconomic cooperation |
| Ensure Sustainable Development | Focus on climate change, green energy, and inclusive growth |
| Improve Financial Regulations | Coordinate regulation of banks, financial markets, and digital currencies |
| Foster International Trade | Reduce barriers and promote fair multilateral trade rules |
| Enhance Global Health Security | Joint efforts for pandemic prevention, vaccines, and health equity |
| Support Digital Transformation | Promote digital infrastructure and innovation across nations |
Presidency of G20 Countries (Recent Years)
The G20 presidency rotates annually among members. The host nation sets the agenda, organizes meetings, and holds the G20 Leaders’ Summit. Each presidency aims to reflect regional priorities within the global context.
| Presidency of G20 Countries (Recent Years) | ||
| Year | Presiding Country | Key Focus/Themes |
| 2020 | Saudi Arabia | Realizing opportunities of the 21st century for all |
| 2021 | Italy | People, Planet, Prosperity |
| 2022 | Indonesia | Recover Together, Recover Stronger |
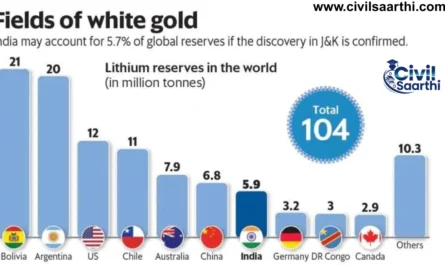
| 2023 | India | One Earth, One Family, One Future |
| 2024 | Brazil | Inclusive growth, energy transition, sustainable development |
| 2025 | South Africa (Upcoming) | Digital economy, Africa’s role in global governance (expected) |
Working Structure of G20 Countries
The G20 Countries operate through several engagement groups and ministerial meetings throughout the year. These working structures ensure that expert input is considered in policy-making before final decisions are taken at the annual summit.
| Working Structure of G20 Countries | |
| Working Level | Purpose |
| Finance Track | Meetings of finance ministers, central bank governors |
| Sherpa Track | Coordinates political aspects, economic policy, and summit declarations |
| Engagement Groups | Includes Civil20, Youth20, Women20, Business20, Think20, Urban20, etc. |
| Ministerial Meetings | Sector-specific meetings (e.g., Health, Digital, Trade, Energy) |
| G20 Secretariat | Temporarily hosted by presiding country for organizing and coordination |
Key G20 Summits and Declarations
Over the years, G20 Countries have made several crucial declarations on climate change, health, finance, and technology. These summits guide the priorities of multilateral organizations like the IMF, WHO, and WTO.
| Key G20 Summits and Declarations | ||
| Summit | Location | Major Outcomes |
| 2008 (First) | Washington D.C. | Coordinated response to global financial crisis |
| 2015 | Antalya, Turkey | G20 Action Plan on terrorism and refugee crisis |
| 2016 | Hangzhou, China | Support for Paris Climate Agreement and digital economy |
| 2020 (Virtual) | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | COVID-19 pandemic response and debt relief for poor countries |
| 2023 | New Delhi, India | Global Biofuel Alliance, Digital Public Infrastructure framework |
Challenges Faced by G20 Countries
Despite their economic power, G20 Countries face internal divisions and external global tensions. These challenges can sometimes weaken collective action and delay multilateral progress.
- Geopolitical Rivalries (e.g., US-China, Russia-West) impact consensus.
- North–South Divide on climate finance and development priorities.
- Unequal Vaccine Access during COVID-19 revealed gaps in health equity.
- Debt Crises in Low-Income Nations need coordinated debt restructuring.
- Digital Governance and AI regulation lack unified global frameworks.
Reforms and Future of G20 Countries
As the global order shifts, G20 Countries are exploring reforms to enhance their relevance, inclusivity, and efficiency. Broadening their engagement with developing nations and addressing cross-border issues is key to their future.
- Greater Role for Global South via African Union’s inclusion (2023).
- Permanent Secretariat Proposal to ensure policy continuity.
- Integration with UN SDGs and climate goals.
- Digital Inclusion Agenda for equitable access to technology.
- Stronger Health Governance in post-COVID world order.
FAQs on G20 Countries
What is the G20?
The G20 is a group of 19 countries and the European Union that work together on global economic issues.
How many countries ,are in the G20?
There are 20 members – 19 countries plus the European Union.
Is India a member of the G20?
Yes, India is a founding member and hosted the 2023 G20 Summit in New Delhi.
What is the difference between G7 and G20?
G7 includes only advanced economies, while G20 includes both advanced and emerging ones.
No, G20 has no permanent secretariat. The presidency rotates annually among its members.
Does the G20 have a permanent headquarters?
No, the G20 does not have a permanent headquarters or a standing secretariat.